Chain Oils
Chains are utilized in applications like conveyors, industrial machinery, and power transmission for certain vehicles. Chain lubricants should penetrate to the wear points in the links to help extend the life of the chain. Lubricants that are tailored for chains will be fortified with anti-corrosive and anti-wear or extreme pressure additives to ensure long-lasting protection even under heavy loading. In high-speed or low-speed chain applications, it may be advantageous for a lubricant to contain a tacky polymer to resist fling-off or dripping, ensuring that the lubricant clings to the chain. For chains in extreme temperature ranges, choose a lubricant based on synthetic base stocks that can better protect under the conditions. PAO or ester-based lubricants, for example, are good choices for these extreme temperatures compared to mineral oil-based lubricants. At extremely high temperatures, one could even consider a “solid” lubricant, like those based on Boron nitride, to avoid heavy carbon deposits associated with fluid lubricants at high temperatures.
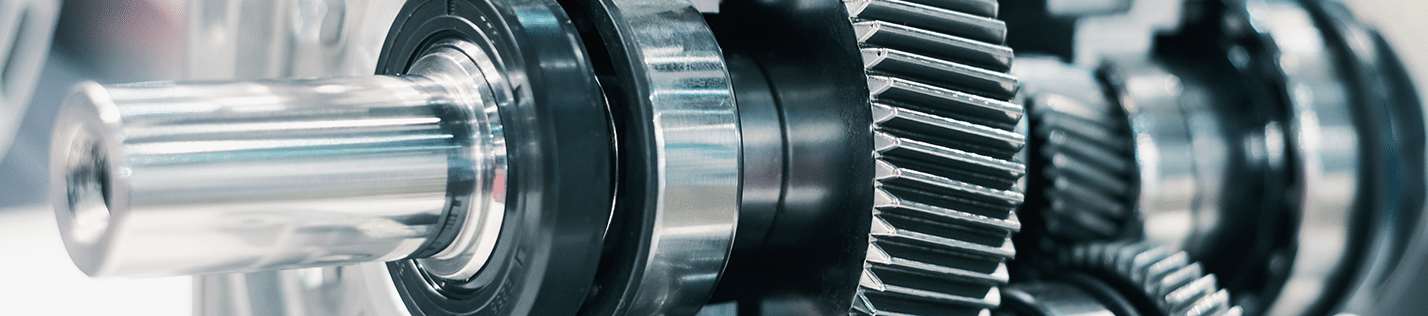
Gear Oils
Gears are commonly found in mining and construction equipment, power generation equipment, and automotive transmissions and differentials. While gear oils will similarly protect against wear and corrosion like chain oils, the important separating factors for these fluids would be the incorporation of more severe extreme pressure (EP) additives and a relatively higher viscosity grade (typically ISO 150 and above). This is necessary as gears are commonly subjected to heavy and sudden loading, like those found in rock crushers. One specialty scenario frequently encountered is the proper lubrication of worm gears. Worm gears experience sliding friction and often contain copper components, unlike most other gear sets which experience mostly rolling friction and are constructed of steel. For worm gear applications, typical gear lubricants won’t provide enough lubricity to aid in the more difficult-to-manage sliding friction and can quickly corrode the copper components. For these applications, a synthetic PAG-based gear oil is the fluid of choice that will provide the superior performance required for worm gears.
Hydraulic Oils
Hydraulic fluids are used mainly as a vehicle for power transmission, allowing a relatively small input of power to result in a relatively large change. Hydraulic power transmission is the basic principle that allows construction equipment like excavators to move large loads with a small amount of power input. Hydraulic fluids also aim to seal and prevent corrosion and wear of the hydraulic system, including the pumps, vanes, and actuators. They are commonly reinforced with antioxidants to extend fluid service life, as well as polymers that serve to increase the temperature range at which they are effectively operating. Among the various types of lubricants, hydraulic oils play a crucial role in machinery operations.
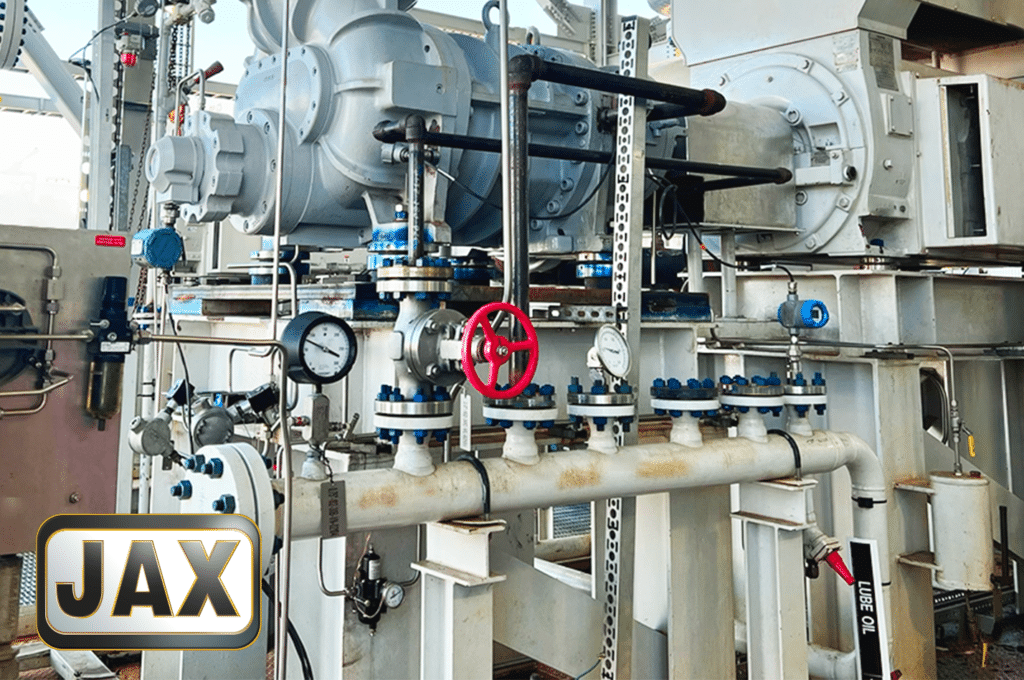
Compressor Oils
Compressor oils are designed to lubricate and seal the internal moving parts of a compressor. Compressors commonly found in industry compress air, refrigerants, or raw materials that eventually become a finished product. Depending on the engineering design of a specific compressor, the lubricating fluid may be in constant contact with the material being compressed, like in the case of HFC compressors. In this example, a lubricant that is miscible with the compressed product at operating temperatures is necessary for proper protection of internal parts. Compressor fluids are differentiated from the other fluids we’ve touched on by the nature of their cleanliness. Compressors have very tight internal spaces to effectively compress the material. If a compressor fluid is filled with materials that deposit on the metal surfaces of the compressor, the effectiveness and service life of the compressor is drastically reduced. Compressor fluids are also typically strengthened with antioxidants and anti-foam additives to help extend fluid life and compressor life, respectively. This makes compressor oils one of the specialized types of lubricants essential for specific machinery.
Understanding the unique demands of each application and taking the right measures helps to safeguard machinery against wear, corrosion, and operational inefficiencies. By choosing the right lubricant from the various types of lubricants, machinery can be protected, and its service life can be extended.
If you have questions about selecting the right lubricant for your unique application or need assistance troubleshooting, reach out on our website, or contact your local representative. Knowing the different types of lubricants and their specific uses can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of your equipment.