Introduction
The term “emulsion” is most often used to describe items we regularly consume. Yogurt, mayonnaise, and whipped cream are classic examples of emulsified foods. Emulsions, in a general sense, are relatively stable mixtures of two liquids that would not mix well under normal circumstances (typically, this refers to oil and water). The emulsification process is straightforward. It involves an emulsifying agent to stabilize small particles of one liquid inside the bulk of another.
In lubricants, product data sheets are often found boasting the ability of an oil to either “demulsify” or emulsify. We will discuss the difference between these terms and key areas where one is desired over the other.
Emulsifying vs. Demulsifying Oils
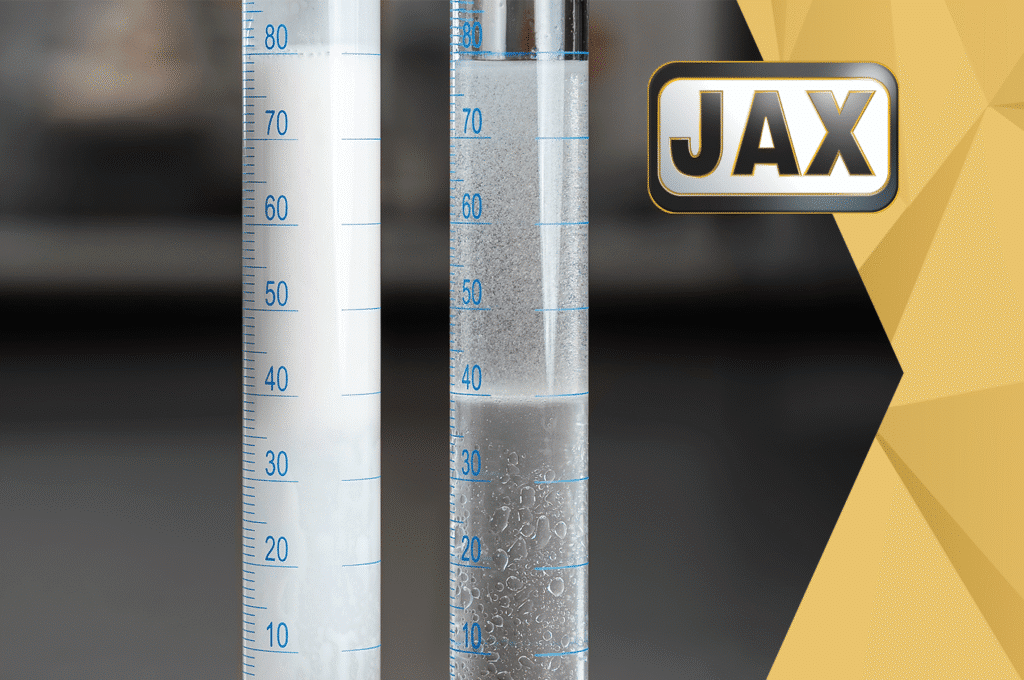
The majority of lubricants on the market are demulsifying by nature. Most lubricants are based on hydrocarbon chains that are naturally immiscible with water, which means they will separate readily from water when mixed. This is important in applications where water would cause severe corrosion to machinery components or reduce the effectiveness of the lubricant. Depending on the specific base stock and additive selection, some lubricants will separate more quickly from water than others. This can be confirmed via ASTM test method D1401. This standardized method mixes 40 ml of water and 40 ml of oil together and measures the amount of time it takes for the oil and water to become separate again. Good demulsifying oils will separate from the oil/water mixture very quickly.
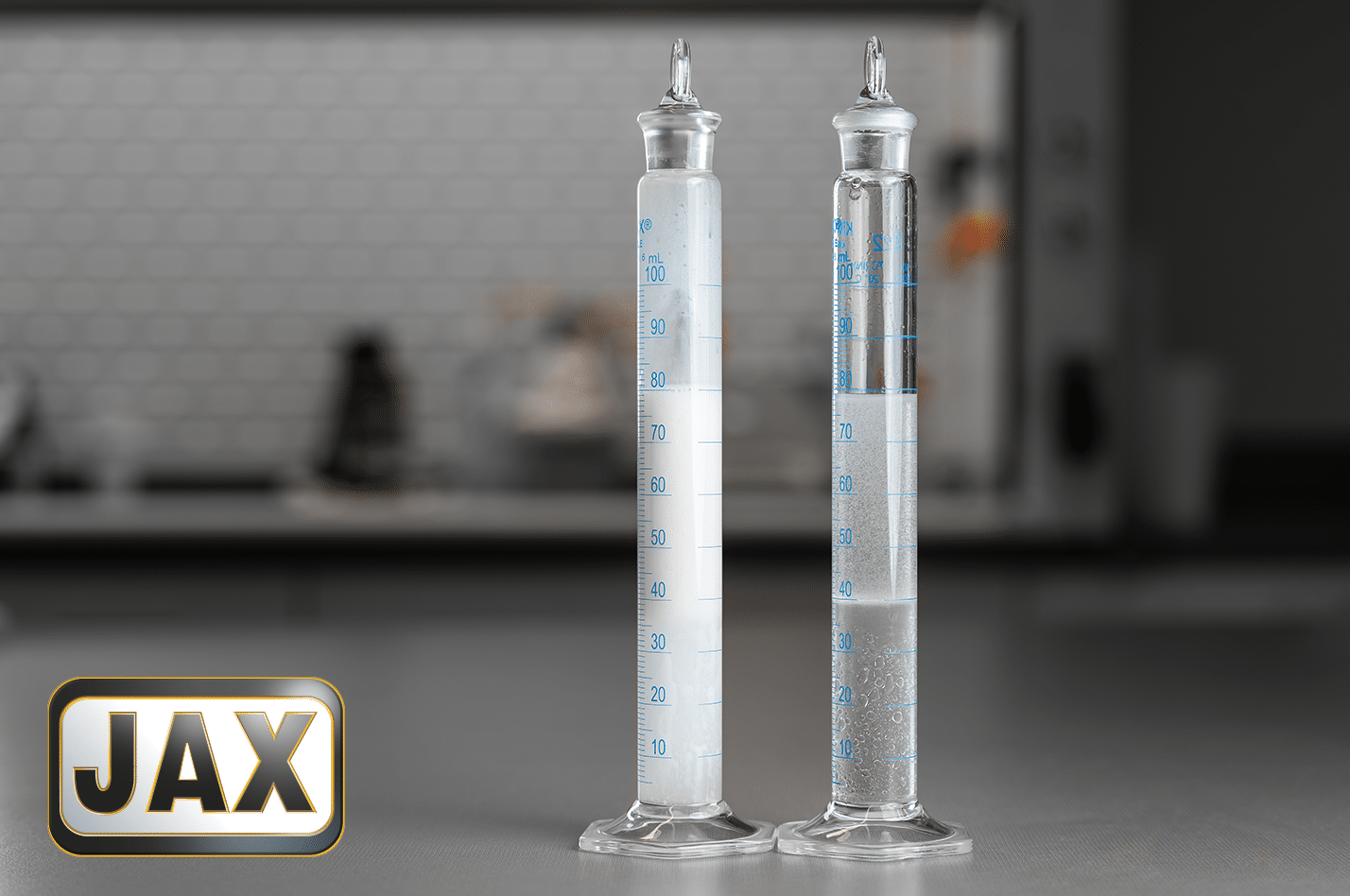

Industrial gearboxes subjected to frequent water contamination are an instance where demulsifying lubricants would be desired. The distinct water layer would accumulate on the bottom of the gearbox near the drain plug, which allows for water to be drained out prior to operating again, ensuring maximum protection for the gearbox with minimal water exposure.
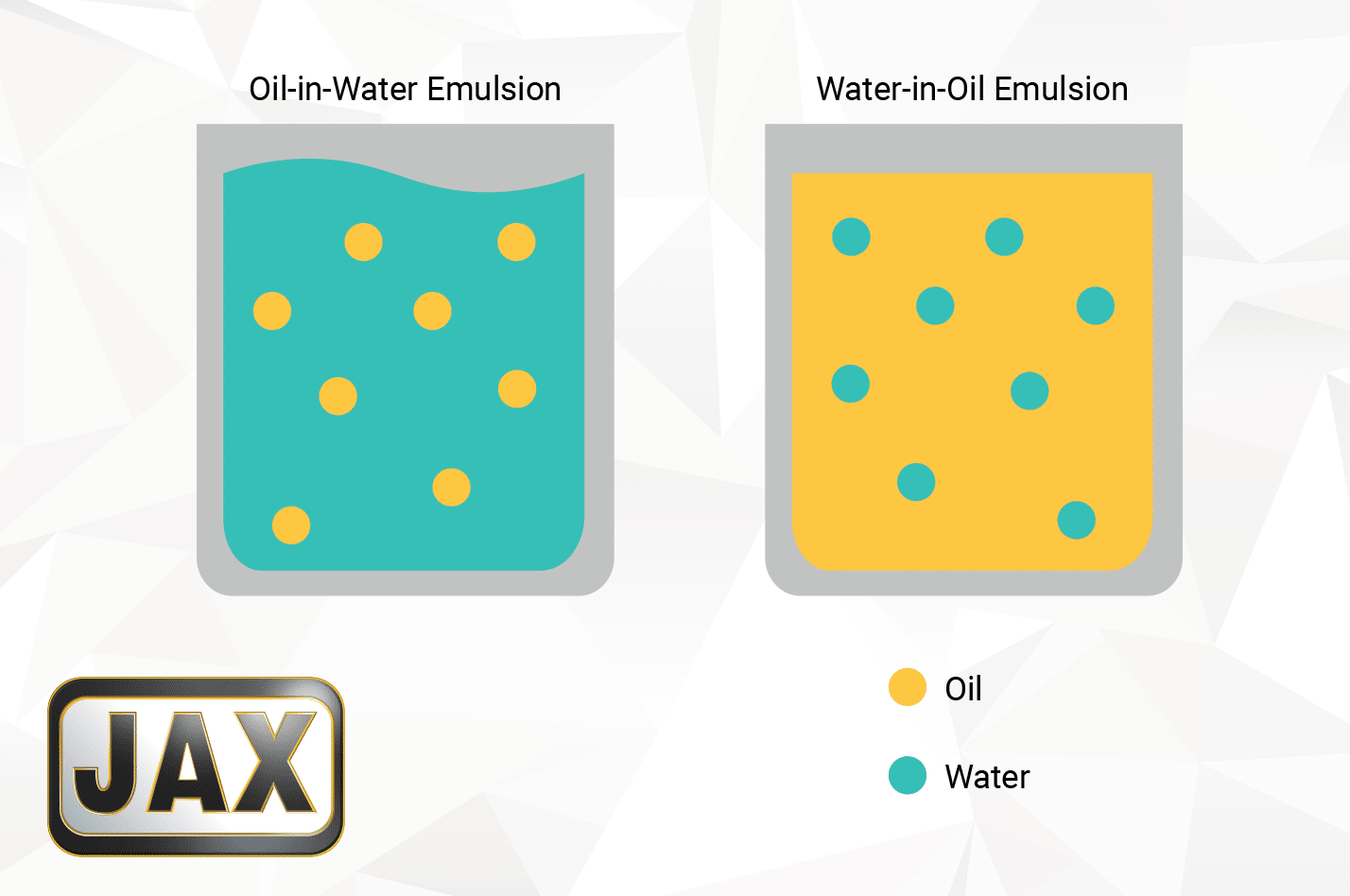
Emulsifying oils, on the other hand, are a special class of lubricants where emulsifying with water is desired and beneficial to the application. There are two distinct lubricant emulsions that dictate the behavior of the fluid: water-in-oil emulsions and oil-in-water emulsions. These emulsions only differ in which fluid is dispersed in the other. The majority of emulsifying lubricants make water-in-oil emulsions, reducing water’s ability to pool and cause corrosion issues or freeze, for example.
Caution is advised when selecting emulsifying fluids, as they behave so differently from traditional lubricants that their emulsifying nature isn’t always desired. High-speed beverage lines canning high-sugar content drinks, for example, are great candidates for using emulsifying lubricants. The emulsifier inside the lubricant can effectively dissolve any excess sugars from contaminating the equipment, which would cause component wear.
Summary
An emulsion is a stable mixture of two immiscible liquids, such as oil and water. In lubrication, emulsions play a critical role in determining a lubricant’s interactions with water. Most industrial lubricants are designed to be demulsifying, meaning they quickly separate from water to prevent corrosion and maintain performance. This is especially important in equipment like gearboxes exposed to water. These properties are measured using standardized tests such as ASTM D1401. Conversely, emulsifying lubricants are specially formulated to carry water, creating stable emulsions that can prevent water pooling and corrosion. While less common, these are useful in specific applications, such as food processing equipment, where emulsifiers can help manage contaminants like sugar. Choosing between emulsifying and demulsifying lubricants depends on the operating environment and the desired protective properties.